ルーティングテーブル
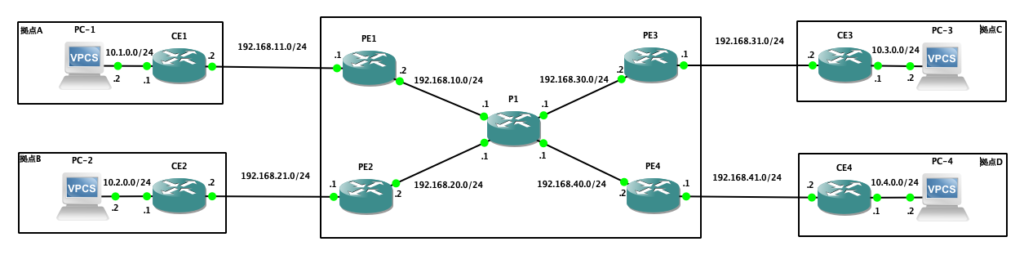
CE1
CE1#sh ip route
Codes: C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.11.1 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.1.0.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.11.1
CE1#
PE1
PE1#sh ip route
Codes: C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 4 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 1.1.1.3 [110/21] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:31, Ethernet0/0
O 1.1.1.2 [110/21] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:31, Ethernet0/0
O 1.1.1.4 [110/21] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:31, Ethernet0/0
O 192.168.30.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:31, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
O 192.168.40.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:31, Ethernet0/0
O 192.168.20.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.10.1, 00:26:32, Ethernet0/0
PE1#
PE1#sh ip route vrf CUST
Routing Table: CUST
Codes: C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 4 subnets
B 10.2.0.0 [200/0] via 1.1.1.2, 13:52:30
B 10.3.0.0 [200/0] via 1.1.1.3, 00:30:50
S 10.1.0.0 [1/0] via 192.168.11.2
B 10.4.0.0 [200/0] via 1.1.1.4, 00:26:34
PE1#
P1
P1#sh ip route
Codes: C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 4 subnets
O 1.1.1.1 [110/11] via 192.168.10.2, 00:32:36, Ethernet0/0
O 1.1.1.3 [110/11] via 192.168.30.2, 00:32:36, Ethernet0/2
O 1.1.1.2 [110/11] via 192.168.20.2, 00:32:36, Ethernet0/1
O 1.1.1.4 [110/11] via 192.168.40.2, 00:32:36, Ethernet0/3
C 192.168.30.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/2
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.40.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/3
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1
P1#
PE1、P1のグローバルルーティングテーブルには、BGPネイバー確立用の経路情報だけがインストールされ、VRF CUSTの経路情報は混在していないことが確認できます。
.png)